Education is key for empowerment. We aim to provide patients and providers with resources to support informed decision making. OPEN offers a wide range of evidence-based materials that highlight the latest best practices for healthcare professionals, patients and their families from pain management to safe storage and disposal of medications.
Co-branding with your organization’s logo is also available for various materials, free of charge. Request today!

Use OPEN’s evidence-based prescribing recommendations for tailored pain management after surgery in adult patients.

Stay up to date with OPEN’s summary of best practices for prescribing after surgery.
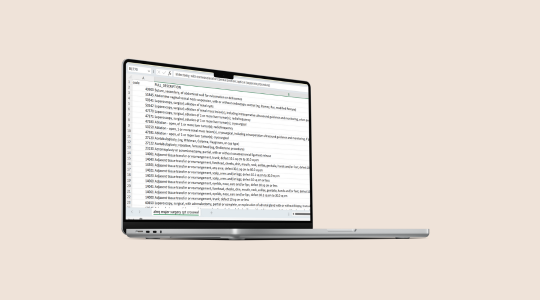
Use this crosswalk to understand the link between individual surgical procedures and all Current Procedural Terminology codes for major surgery in the 2014-2022 AHRQ algorithm.

Learn how to prepare for surgery and to help manage pain after surgery.

As a healthcare provider, learn evidence-based approaches to help manage your patient’s pain after surgery.

Learn ways to manage pain after surgery such as: over-the-counter medications, non-medication strategies, and opioids, if prescribed.

Learn how to help manage or reduce your pain and anxiety through various techniques.

Explore 4 evidence-based reasons to improve opioid prescribing practices after surgery.

Explore OPEN’s process to create and evaluate opioid prescribing recommendations.

Explore the five Levels of evidence to use while making educated determinations about prescribing and care.

Learn more about how risky substance use impacts patients having surgery and best practices for identification and coordination of care for those with risky use.

Learn more about prescribing acetaminophen and NSAIDs for pain management after surgery.

Intended to improve communication between providers and patients about the risks and benefits of opioid therapy for chronic pain, improve the safety and effectiveness of pain treatment, and reduce the risks associated with long-term opioid therapy, including opioid use disorder and overdose.